Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
How Botox Affects Facial Muscles
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to smooth wrinkles and fine lines on the face by temporarily paralyzing facial muscles.
The science behind Botox lies in its active ingredient, botulinum toxin, which is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. When injected into the correct muscle groups, Botox blocks the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, thereby inhibiting muscle contractions.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles are primarily due to its ability to relax facial muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines. The most commonly targeted muscles for Botox injections include:
- Forehead lines: The frontalis muscle in the forehead causes vertical lines between the eyebrows, which can be reduced or eliminated with Botox.
- Frown lines: The procerus and corrugator muscles between the eyebrows can be relaxed to reduce horizontal lines across the face.
- Crow’s feet: The orbicularis oculi muscle around the eyes causes wrinkles and fine lines that can be softened or eliminated with Botox.
Botox works by blocking the nerve signals that cause these muscles to contract, resulting in a reduction in wrinkle depth. When a muscle is paralysed, it loses its ability to move and contract, which leads to a decrease in wrinkles and fine lines.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how Botox affects facial muscles:
- When a nerve signal reaches the end of a muscle fibre, acetylcholine is released, stimulating the muscle contraction.
- The botulinum toxin in Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, preventing the muscle contraction from occurring.
- The muscle becomes paralysed, and wrinkle depth decreases as a result.
The effects of Botox are temporary and typically last for 3-6 months. This is because the body gradually breaks down the botulinum toxin, allowing nerve signals to resume and muscle contractions to restart. Repeated Botox treatments can help maintain the desired effect.
Understanding how Botox affects facial muscles provides valuable insights into its mechanism of action and potential benefits for reducing wrinkles and fine lines.
Botox is a neurotoxin protein that has become a popular non-surgical solution for smoothing wrinkles and fine lines on the face.
The mechanism of action of Botox involves the temporary relaxation of facial muscles, which reduces wrinkle appearance and minimizes the signs of aging.
Botox works by blocking the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which is responsible for transmitting signals from nerve cells to muscle fibers.
This blockage prevents the muscles from contracting and tightening, resulting in a smooth and relaxed appearance.
The facial muscles that are affected by Botox include those in the forehead, between the eyebrows, around the eyes, and on the mouth.
When these muscles contract, they pull on surrounding skin, causing wrinkles and fine lines to form.
By relaxing these muscles, Botox reduces the appearance of these wrinkles, resulting in a smoother and more youthful complexion.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles are most noticeable when it is injected into areas with high muscle activity.
In the forehead, for example, Botox can reduce horizontal lines between the eyebrows, known as glabellar lines, by relaxing the corrugator and procerus muscles.
Around the eyes, Botox can relax the orbicularis oculi muscle, which is responsible for closing the eyelids and reducing puffiness.
In the mouth, Botox can relax the orbicularis oris muscle, which helps to minimize lip lines and wrinkles.
As Botox works its way through the system, it begins to break down into smaller molecules that are then excreted from the body.
This process typically takes several weeks, after which the effects of Botox on facial muscles begin to wear off.
However, some patients may require repeated injections every few months to maintain the desired effect.
The frequency of injections depends on a variety of factors, including the individual’s muscle activity and wrinkle depth.
Additionally, some people may experience residual effects from previous Botox treatments that can last for several weeks after the treatment has been completed.
Overall, Botox is a highly effective treatment for smoothing wrinkles and fine lines on the face, but it’s essential to have realistic expectations about its duration of effect.
Botox should only be used under the guidance of a qualified medical professional who can assess individual needs and determine the best course of treatment.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, works by targeting facial muscles that are responsible for causing wrinkles and fine lines.
The American Academy of Dermatology explains that botulinum toxin (Botox) is a neurotoxin that temporarily paralyzes muscle activity.
This temporary paralysis is achieved by blocking nerve signals that cause muscle contractions, resulting in a decrease in muscle movement and relaxation of the facial muscles.
The primary mechanism behind Botox’s effect on facial muscles involves its ability to inhibit the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals from nerve cells to muscle fibers, instructing them to contract and move.
When acetylcholine is released, it binds to receptors on the surface of muscle cells, triggering a series of reactions that ultimately lead to muscle contraction.
In the case of Botox, when the toxin is injected into a facial muscle, it binds to acetylcholine receptors and blocks their action, effectively halting muscle contractions.
This blockage results in a reduction of muscle activity, leading to a decrease in wrinkle formation and a smoother appearance.
Specifically, Botox is administered to the following facial muscles:
– Frontalis: This muscle runs from the forehead to the eyebrows and is responsible for raising the eyebrows.
– Procerus: This muscle runs between the nose and the upper lip and is responsible for frowning and creating horizontal lines on the face.
– Orbicularis oculi: This muscle surrounds the eye and is responsible for closing the eyelids and creating crow’s feet.
By targeting these muscles, Botox helps to reduce or eliminate wrinkles and fine lines associated with facial expressions, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
The American Academy of Dermatology emphasizes that the effects of Botox are temporary, typically lasting between three and six months, depending on individual factors such as muscle activity and skin type.
It is essential to follow recommended treatment schedules and guidelines to ensure optimal results and minimize side effects.
Botox is a popular non-surgical cosmetic treatment used to relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles can be attributed to its unique mechanism of action, which involves temporarily paralyzing the muscle fibers responsible for wrinkle formation.
Botox contains a toxin derived from the bacterium _Clostridium botulinum_, which is purified and concentrated to create a highly potent and safe formulation.
When administered into the facial muscles, Botox works by binding to the *acetylcholine receptors* on the muscle cells, preventing the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contraction.
As a result, the facial muscles become weakened and unable to contract, leading to a smooth and relaxed appearance.
The facial muscles targeted by Botox include:
- *Forehead lines**: caused by the corrugator supercilii and procerus muscles, which are responsible for frowning and squinting
- *Frown lines between the eyebrows**: caused by the procerus and corrugator supercilii muscles
- *Crow’s feet**: caused by the orbicularis oculi muscle surrounding the eye
- *Lip lines**: caused by the orbicularis oris muscle surrounding the mouth
- *Bunny lines**: caused by the zygomaticus major and minor muscles, which pull the corners of the mouth downward
- *Marionette lines**: caused by the depressor anguli oris and buccinator muscles, which are involved in facial expressions such as smiling and laughing
- *Facial asymmetry**: Botox can also be used to balance out facial features by relaxing asymmetrical muscles
The success of Botox depends on the skill and experience of the practitioner, as well as the specific muscle targets and dosage.
A typical treatment session involves administering multiple injections into specific muscle groups using a fine needle.
Results from Botox treatments are typically noticeable within 2-4 days and can last for 3-6 months, depending on individual factors such as muscle mass and metabolism.
Repeating Botox treatments at regular intervals is necessary to maintain the desired effects and prevent muscle reactivation.
It’s worth noting that while Botox is highly effective for wrinkle reduction, it may not address deeper wrinkles or folds, which require more invasive procedures like facelifts or dermal fillers.
In addition, Botox can have some temporary side effects, such as bruising, swelling, and eyelid drooping, but these are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to smooth out wrinkles and fine lines on the face by temporarily paralyzing facial muscles.
Fine lines and wrinkles are caused by repetitive muscle contractions, which create folds and creases in the skin over time.
When we smile, frown, or make other facial expressions, the corresponding muscles contract to produce the desired movement.
However, these repeated contractions can lead to fatigue in the muscles, causing them to become less effective at producing the desired motion.
This reduced effectiveness can result in the formation of wrinkles and fine lines, particularly around the eyes, forehead, and mouth areas.
The facial muscles responsible for creating expressions are grouped into three primary muscle categories: the orbicularis oculi (eye), frontalis (forehead), and zygomaticus major and minor (mouth).
When Botox is administered to these areas, it blocks the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which normally signals muscle contractions.
This blockade prevents the muscles from contracting as they normally would, effectively paralyzing them for several months.
The resulting paralysis causes the muscle to relax and contract less frequently, allowing the skin to smooth out and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The effect of Botox on facial muscles can be seen in the reduction of repetitive movements that contribute to wrinkle formation, such as:
– Eyebrow lifting and furrowing
– Forehead wrinkling
– Lip raising and pursing
– Smile lines and crow’s feet
By targeting these specific muscle groups, Botox can effectively reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, providing a smoother, more youthful-looking complexion.
The temporary nature of Botox makes it an attractive option for those who want to temporarily relax facial muscles without making a long-term commitment.
However, regular Botox injections are often necessary to maintain the desired effects, as muscle contractions can return over time.
Furthermore, Botox should only be administered by a qualified and licensed practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles and fine lines on the face.
The process of how Botox affects facial muscles is quite fascinating and involves understanding the anatomy of the human face, particularly the muscles that control movement and expression.
Research from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) suggests that facial muscles, particularly those in the forehead, around the eyes, and between the eyebrows, are responsible for creating these unwanted lines.
The most commonly affected areas by Botox injections are the corrugator supercilii muscle, which runs from the nose to the eyebrow bone, and the procerus muscle, which is located between the eyebrows.
These two muscles work together to create furrows and wrinkles between the eyebrows and above the eyes, known as glabellar lines.
Botox works by blocking the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which signals the muscles to contract. When Botox is injected into the facial muscles, it temporarily paralyzes them, preventing them from contracting and causing wrinkles and fine lines.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles are immediate and can last for several months, typically between 3-6 months, depending on individual factors such as muscle strength and metabolism.
When Botox is injected into the muscles, it can take a few days to a week or so for the full effect to be visible. During this time, the muscles may still twitch or experience some residual weakness.
However, once the full effect of Botox is achieved, wrinkles and fine lines caused by these muscles can start to fade away, resulting in smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
The process of how Botox affects facial muscles has been extensively studied through various research studies, including those conducted at UCLA.
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology found that Botox injections resulted in significant reduction of wrinkle depth and surface area between the eyebrows, as well as a decrease in muscle activity.
Another study published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology used functional MRI to investigate changes in brain activity after Botox injections. The results showed that Botox reduced activity in areas of the brain responsible for facial expressions and emotional control.
This research suggests that Botox not only affects the physical appearance of wrinkles but also has a broader impact on our emotional and cognitive responses, highlighting its complex mechanisms and potential benefits.
Botox works by temporarily paralyzing facial muscles, thereby reducing wrinkles and fine lines on the face.
This effect is achieved through a process called neurotoxin injection, where small amounts of Botox are administered into specific muscles to block nerve signals that control muscle movement.
The most commonly treated areas for wrinkles include the frown lines between the eyebrows, crow’s feet around the eyes, and forehead lines.
Botox affects the facial muscles by binding to neurotransmitters, specifically acetylcholine, which is released by motor neurons to signal muscle contractions.
This binding causes a decrease in muscle activity, resulting in a relaxation of the targeted muscles, leading to reduced wrinkles and fine lines.
For instance, when Botox is injected into the muscles between the eyebrows, it blocks the release of acetylcholine, which normally signals the orbicularis oculi muscles to contract, thereby reducing frown lines.
A similar effect occurs when Botox is administered into the crow’s feet area, where it relaxes the zygomaticus major muscle, reducing smile lines and wrinkles around the eyes.
Another common site for Botox treatment is the glabella region, where it targets the procerus and corrugator supercilii muscles to smooth out forehead lines and creases.
The efficacy of Botox in smoothing wrinkles has been extensively studied and documented, with numerous clinical trials demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing facial fine lines and wrinkles.
Studies have shown that Botox can effectively reduce wrinkle depth by up to 90% within 30 days of treatment, with results typically lasting for 3-6 months before requiring re-treatment.
However, it’s essential to note that the duration of Botox efficacy varies depending on individual factors, such as muscle activity, lifestyle habits, and skin type.
Some people may experience more significant improvements in wrinkle appearance than others, while some individuals may require multiple injections or a higher dose to achieve optimal results.
Additionally, the effectiveness of Botox can be influenced by other facial features and muscles not directly targeted by treatment, such as the nasolabial folds or marionette lines.
The limitations of Botox include potential side effects, such as droopy eyelids (ptosis), facial asymmetry, and eyelash changes, which are rare but can occur in some individuals.
Furthermore, repeated use of Botox may lead to resistance or habituation, where the body adapts to the toxin by changing its neural pathways, reducing efficacy over time.
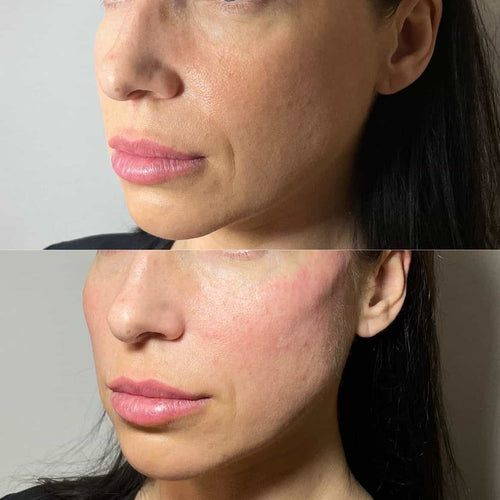
Another limitation is that Botox cannot address deeper wrinkles or skin laxity, which require surgical intervention for effective treatment.
Additionally, Botox may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions, such as eyelid spasms, eye problems, or neurological disorders, which can interact negatively with the toxin.
To minimize risks and maximize benefits, it’s crucial to choose a qualified healthcare professional experienced in administering Botox injections and following proper treatment protocols.
A thorough consultation, including a comprehensive medical history and skin analysis, is essential to determine if Botox is an effective solution for individual wrinkle concerns.
Botox is a widely used cosmetic treatment that has become a staple in many people’s skincare routines. It is administered via a simple injection, typically between the eyebrow bone and the forehead, or along the oral commissure (the corner of the mouth). The treatment involves the use of neurotoxin _Botulinum Toxin_ , which temporarily relaxes facial muscles to reduce wrinkles and fine lines.
The primary mechanism of action of Botox is through the inhibition of the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from the nerve endings that stimulate muscle contractions. When _acetylcholine_ binds to its receptors, it triggers a signal that causes the muscles to contract and relax. By blocking the release of _acetylcholine_, Botox prevents these signals from being sent to the muscles, resulting in temporary paralysis.
The facial muscles affected by Botox are highly innervated, meaning they contain a large number of nerve endings. The most common areas treated with Botox include the frontalis muscle, which is responsible for raising the eyebrows and frowning; the orbicularis oculi muscle, which surrounds the eye and causes eyelid closure and eyebrow movement; and the oralis oris muscle, which is involved in smiling.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles can be seen almost immediately, with noticeable smoothing of wrinkles and fine lines within a few days. The duration of action varies depending on the area treated and the individual’s muscle mass, but most effects last between three to four months before wearing off.
One of the benefits of Botox is its reversibility; once the effects wear off, facial muscles regain their natural function, and wrinkles return to their pre-treatment state. Additionally, Botox does not cause permanent muscle damage or scarring.
While Botox can be highly effective in reducing wrinkles, it’s essential to maintain realistic expectations. It may not completely eliminate deep wrinkles or lines caused by repetitive facial expressions, such as crow’s feet or forehead furrows. Additionally, repeated use of Botox may lead to the development of antibodies against the _Botulinum Toxin_, which can cause a less effective response over time.
It’s also worth noting that Botox is not suitable for everyone; individuals with certain medical conditions, such as myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton Syndrome, or duodenal ulcers, should avoid treatment. Furthermore, pregnant and breastfeeding women should use caution when considering Botox, as the effects on fetal development and infant safety are not well understood.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige
In summary, while Botox is an effective treatment for smoothing wrinkles by temporarily relaxing facial muscles, its effects are indeed temporary and require repeated administration to maintain results. By understanding how Botox works and its limitations, individuals can make informed decisions about their cosmetic treatments and achieve the desired level of wrinkle reduction.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines.
The effects of Botox on facial muscles are quite fascinating, and understanding how it works can provide insight into why it’s such an effective treatment.
When Botox is injected into a muscle, it blocks the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine, which signals the muscle to contract.
This relaxation of the muscle leads to a decrease in wrinkle depth and volume, as the muscles are no longer able to move and pull on surrounding skin.
The study published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) indicates that Botox can provide a significant reduction in wrinkle depth and volume over periods ranging from 3 to 12 months.
However, repeated treatments may be necessary to maintain desired results, as the effects of Botox typically wear off after several months.
The length of time that Botox remains effective can vary depending on a number of factors, including:
– The location and type of muscle being treated
– The dose of Botox used
– Individual variability in metabolism and response to treatment
For example, Botox is commonly used to treat facial wrinkles caused by the muscles around the eyes (crow’s feet), forehead (horizontal lines), and mouth (smile lines).
The study found that repeated treatments can maintain desired results for a period of time, but the effects may wear off over time.
This wearing off is due to:
- Breakdown of the Botox toxin by the body’s enzymes
- Spread of the toxin to other areas of the body beyond the treated muscle
- Development of antibodies against the toxin, which can neutralize its effects
Despite these limitations, Botox remains a popular and effective treatment for smoothing wrinkles and fine lines.
The study also highlights the importance of finding an experienced and qualified healthcare professional to administer Botox injections.
This is crucial in ensuring accurate placement of the toxin and minimizing potential side effects.
Read more about BeyBey Name here. Read more about On the Carpet here. Read more about Crimson Hill here. Read more about The First Come First Served here. Read more about One One Three Online here.
- Marionette Lines Filler Near Long Ditton, Surrey - May 9, 2025
- Can Kratom Energy Drinks Help With Social Anxiety? - May 7, 2025
- Downturned Smile Treatment Near Windlesham, Surrey - May 7, 2025

